Inside SDSU’s AI-Powered First-Year Seminar: Life Tree Projects, Microcredentials, and Real-World Skills
Introduction
College is a pivotal time for self-discovery and goal-setting. At San Diego State University (SDSU), this journey begins with a forward-thinking approach that incorporates hands-on training in artificial intelligence and Adobe’s creative tools. The First Year Seminar (FYS) now integrates AI literacy and Adobe Express into a foundational project, enabling thousands of new students to develop responsible, creative, real-world skills from the very start.
Why This Matters Now
- Core Workplace Skill: AI has evolved from a niche technology to a standard expectation. Employers increasingly seek graduates proficient in using AI tools ethically and effectively.
- Essential Communication Skills: Visual storytelling and communication are critical across various fields, including health, engineering, business, and the arts.
- Marketable Competencies: Microcredentials and badges allow students to showcase specific skills to future employers and internships.
SDSU’s innovative approach effectively combines these elements into a student-friendly experience that encourages creativity, self-reflection, and responsible technology use.
What’s New in SDSU’s First-Year Seminar
Starting in fall 2025, over 4,000 students enrolled in more than 228 course sections will learn the fundamentals of ethical AI and digital storytelling. They’ll also earn the SDSU AAAI Microcredential and work on projects using Adobe Express. The initiative aims to scale by training over 75 instructors, ultimately supporting more than 5,700 students each year.
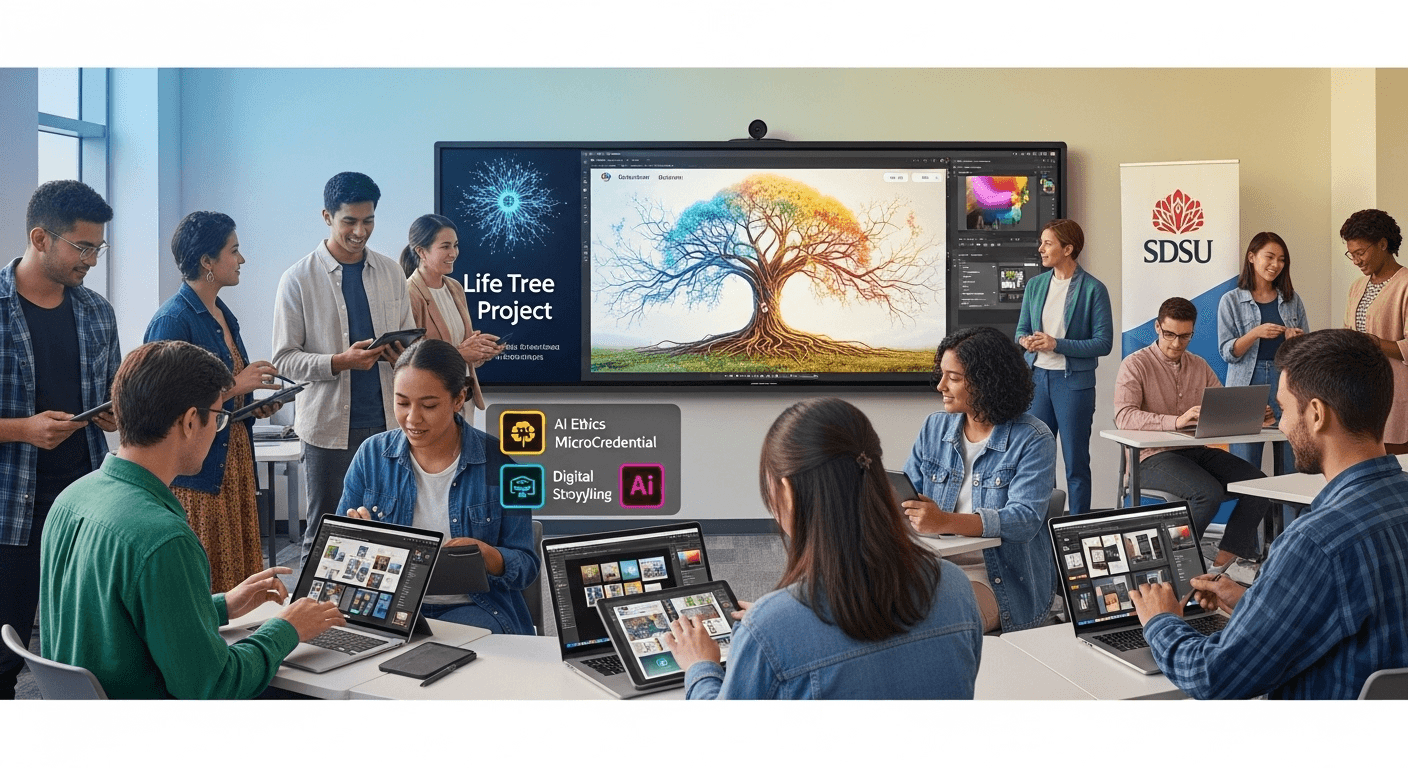
A Keystone with Purpose: The Life Tree Project
The seminar revolves around a semester-long assignment called the Life Tree project. Students will map out their roots, values, and future aspirations, transforming this narrative into a shareable portfolio piece using Adobe Express. This blend of creativity, reflection, and practicality equips students with a tangible story that highlights their skills and aspirations. The project also introduces students to the generative AI features within creative tools, emphasizing the importance of disclosure, fairness, and transparency.
Ethical AI is the Throughline
The course goes beyond tool demonstrations; it emphasizes responsible AI use. Students learn when and how to employ AI, the importance of disclosure, limitations of technology, and the significance of addressing bias, privacy, and accuracy. These practices align with SDSU’s broader AI guidelines as well as the California State University (CSU) system’s mission to expand equitable access and training in AI.
Microcredentialing, Made Meaningful
- AAAI Microcredential: SDSU’s Academic Applications of AI program provides training for students, faculty, and staff on the effective and ethical use of generative AI through short, engaging modules. As of September 2025, over 6,600 participants have engaged with the program, earning badges upon completion.
- Adobe GenAI Badges: Students can also earn optional badges that recognize their communication, technology, and creativity skills developed through Adobe Express and Firefly. Adobe Education offers several micro-badges via Credly, showcasing foundational skills for prospective employers.
Why Adobe, and Why Now
As an Adobe Creative Campus, SDSU was named one of Adobe’s first Creative Campus Innovators in 2025, acknowledging the Life Tree project’s innovative blend of storytelling, Adobe Express, and responsible AI use. This recognition underscores the seminar’s role in enhancing creative confidence and career preparedness across various disciplines.
How the CSU System is Leaning In
Earlier this year, the CSU initiated a public-private partnership to deliver AI tools, training, and apprenticeships systemwide, collaborating with companies like Adobe, Microsoft, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. SDSU has been at the forefront of this initiative, trialing microcredentials and implementing campus guidelines that encourage responsible AI use while safeguarding privacy and academic integrity.
What Students Actually Learn in FYS
- Foundations of AI: Understanding how modern AI systems function and their limitations.
- Ethical Use: Recognizing when to credit AI contributions, how to verify outputs, and avoiding biases.
- Creative Communication: Crafting pages, videos, and graphics with Adobe Express, utilizing AI tools responsibly.
- Reflective Practice: Expressing values, goals, and choices through the Life Tree project.
- Portfolio Building: Presenting work in ways employers recognize, earning optional digital badges.
Connecting to Career Readiness
Employers seek graduates who can communicate effectively, think critically, collaborate, and utilize technology responsibly. These skills align with the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE) career readiness competencies, such as communication, critical thinking, teamwork, professionalism, leadership, equity and inclusion, technology, and self-development. The seminar’s AI and Adobe components enable students to practice and document progress in these areas.
What Responsible AI Looks Like in Practice
- Cite and Explain Use: Students learn to disclose how AI has contributed to their work.
- Keep Humans in the Loop: AI may draft ideas, but students are responsible for editing and fact-checking.
- Respect Creators: Adobe’s Content Credentials and training preferences guide students on how to communicate the usage of their work with GenAI.
A Student-Centered Support Network
The course is backed by a Creative Influencer and Peer Mentorship Network, facilitated by the SDSU Story Lab. Students who complete the microcredential can become peer coaches, hosting workshops and supporting campus showcases, thus fostering community alongside skill development.
Scaling Without Losing the Human Touch
While implementing a widespread initiative can be challenging, SDSU focuses on faculty development, shared rubrics, and adaptable templates to meet various disciplines’ needs. This collaborative approach ensures academic integrity, encourages ethical use, and maintains consistent learning outcomes as the program evolves.
Evidence from Peer Campuses
SDSU isn’t the only institution witnessing the benefits of integrating creative tools with purposeful teaching. A recent analysis at the University of Texas at San Antonio revealed improved student performance in courses using Adobe tools, with a higher proportion of students earning A and B grades compared to those in non-Adobe sections. This growing body of evidence supports the idea that creative and authentic assessments can enhance student motivation and outcomes.
Inside the AAAI Microcredential: What to Expect
- Duration: 2–4 hours of modular content that can be completed at your own pace.
- Real-World Activities: Practical prompts that mirror academic and workplace scenarios.
- Ethics Focus: Emphasis on ethics, disclosure, and accuracy verification.
- Digital Badge: A badge that signifies readiness to responsibly use generative AI at school and work.
- Continued Learning: Opportunities for further education through Adobe micro-badges and SDSU workshops.
A Closer Look at Adobe Express in the Seminar
Adobe Express offers students a user-friendly platform to create portfolio-quality pages, short videos, and social graphics without extensive training. With built-in generative features for imagery and design elements, students can quickly brainstorm, visualize, and refine their work with a critical human touch. Instructors focus on assessing communication clarity, ethical AI use, and process documentation rather than just the final product.
How Instructors Make It Work Across Disciplines
- Business: Crafting brand stories and pitch presentations that connect values to strategy.
- Engineering: Creating visual explanations of design decisions, including trade-offs and test results.
- Health: Developing infographics on patient education topics, ensuring clear citations and bias checks.
- Arts and Humanities: Producing multimedia narratives that link personal stories to cultural contexts.
- Sciences: Composing data storytelling pages that summarize methods, results, and implications.
Academic Integrity When AI is Involved
SDSU emphasizes principles of transparency, privacy, and accuracy throughout the course. Instructors clarify acceptable AI usage, instruct on how to disclose contributions, and promote proper documentation of prompts and outputs. Students utilize AI as a supportive tool, not a shortcut, ensuring facts and sources are verified. This stability allows for productive exploration of AI while maintaining trust and integrity.
For Students: How to Maximize Your Life Tree Project
- Start with Your Values: Write a brief paragraph about what matters to you and why.
- Map Your Branches: Explore education, career interests, communities, and causes you want to champion.
- Draft with AI, Decide as a Human: Use AI for brainstorming but ensure the final piece reflects your voice.
- Show, Don’t Just Tell: Include visuals, video clips, or data snapshots to make your story compelling.
- Be Transparent: Acknowledge where AI assisted you and include reflections on your process.
- Seek Feedback: Share drafts with peer mentors for constructive critique.
For Faculty: A Quick Checklist to Adapt the Model
- Clarify AI Policy: Define acceptable AI use and provide examples.
- Offer Templates and Rubrics: Supply a framework focused on communication, ethics, and reflection.
- Encourage Disclosure: Build a workflow that includes process documentation.
- Use Low-Stakes Milestones: These keep students engaged and ease anxiety.
- Invite Peer Mentors: Organize mini-workshops to enhance learning and motivation.
What This Means for Employers and Internships
As students graduate into workplaces where AI is becoming commonplace, the combination of ethical AI literacy and visual storytelling will prove invaluable. These skills are critical for roles that require documenting decisions, clearly conveying complex ideas to non-experts, or collaborating with stakeholders on proposals. Microcredentials and badges provide hiring managers with clear signals of competencies beyond traditional course titles.
How This Fits into the Bigger CSU Picture
The CSU’s AI Workforce Acceleration initiative aims to ensure equitable access to secure tools, shared training, and partnerships across 23 campuses. SDSU’s pioneering work with AAAI and the FYS Life Tree project serves as a model for integrating system-wide momentum into transformative classroom experiences that enhance learning outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Will every first-year student work with AI and Adobe tools?
Yes, the First Year Seminar integrates ethical AI training and Adobe Express across numerous sections, with plans to reach over 5,700 students annually as faculty training grows. - What exactly is the AAAI Microcredential?
It’s a concise, practical program focused on the academic applications of AI developed at SDSU. It covers how AI functions, promotes responsible usage, explores application discovery, and delivers a digital badge upon completion. Over 6,600 have participated across the CSU by September 2025. - Do these badges matter to employers?
While badges do not guarantee job placement, they enable students to demonstrate specific skills. The content aligns with widely recognized NACE competencies such as communication, critical thinking, and professionalism. - How is privacy protected when using AI?
SDSU and CSU prioritize responsible and secure AI use. This initiative ensures partnerships provide enterprise-grade tools and guidelines that safeguard privacy, academic integrity, and data security. - How do creators get credit when students use GenAI-generated media?
Adobe’s Content Credentials facilitate the attachment of provenance and usage preferences to creative works, allowing creators to indicate how their content may be utilized by supported generative AI models.
What Success Looks Like
- Students graduate from their first semester with a polished artifact that highlights their values, goals, and communication skills.
- Instructors witness more authentic, reflective work accompanied by clear documentation of the creative process and sources.
- The university effectively scales AI literacy while enforcing shared expectations and supportive resources.
- Employers receive clear indications of students’ practical, ethical, and creative skill development.
The Bottom Line
SDSU’s First Year Seminar isn’t merely about teaching students to navigate AI tools. It equips them to think critically, create intelligently, and communicate with integrity. By combining reflective storytelling, responsible AI usage, and accessible design tools, this program offers first-year students a crucial head start on the skills necessary for success in college and beyond.
Thank You for Reading this Blog and See You Soon! 🙏 👋
Let's connect 🚀
Latest Insights
Deep dives into AI, Engineering, and the Future of Tech.

I Tried 5 AI Browsers So You Don’t Have To: Here’s What Actually Works in 2025
I explored 5 AI browsers—Chrome Gemini, Edge Copilot, ChatGPT Atlas, Comet, and Dia—to find out what works. Here are insights, advantages, and safety recommendations.
Read Article


